Ethics Toolbox
The Practical Ethics Toolbox responds to the crucial necessity of AI introduced in Law Enforcement with the potential to generate benefits in efficiency and accuracy, bringing positive change to European Law Enforcement Agencies’ (LEAs) operational capacity. However, at the same time, AI generates also great risks for fundamental rights and democracy. To mitigate risks and create a just, sustainable and inclusive European AI culture for Law Enforcement, it is important to understand what AI ethics is and how it applies these institutions.
The Toolbox comprises three resources that integrate the multiple perspectives of ethics and AI through LEAs’ space. The first resource is a collection of educational videos exploring the intricate relationship between AI and ethics within the context of policing. The second resource constitutes three ethics cases that explore AI in law enforcement, providing awareness of the ethical implications and information about AI’s applications, potential benefits and risks in policing. The third resource is an interactive visualisation of four groups of taxonomies. In the taxonomies, users can find specific terms and documents of the work accomplished under the four popAI project thematics.
Educational Videos
These videos aim to provide valuable insights and enhance comprehension of the ethical considerations regarding AI’s use in law enforcement. Each video tackles various aspects of AI in policing, answering crucial questions and providing clarity on its implications. With these videos, viewers can gain fundamental knowledge to understand the ongoing debates in the field, participate in well-informed conversations, and contribute to the discussion on AI’s role in law enforcement.
Educational Video 1
This video is the presentation of the series of eight educational videos with the objective to spotlight the main doubts, implications, debates and topics regarding ethics in the implementations of AI in the Law Enforcement Agencies.
popAI is funded by the Horizon 2020 Framework Programme of the European Union for Research and Innovation. GA number: 101022001.
Educational Video 2
This video details the difference of ethics and morality and its relation with the LEAs space.
popAI is funded by the Horizon 2020 Framework Programme of the European Union for Research and Innovation. GA number: 101022001.
Educational Video 3
This video talks about the relationship between AI and ethics through policing. The video takes into consideration the possible risks and implications of the use of AI in such complex scenarios.
popAI is funded by the Horizon 2020 Framework Programme of the European Union for Research and Innovation. GA number: 101022001.
Educational Video 4
This video explains how bias can be avoid during the development of AI algorithms.
popAI is funded by the Horizon 2020 Framework Programme of the European Union for Research and Innovation. GA number: 101022001.
Educational Video 5
This video presents the important integration of accountability, traceability and auditability of the AI.
popAI is funded by the Horizon 2020 Framework Programme of the European Union for Research and Innovation. GA number: 101022001.
Educational Video 6
This video highlights the important question of “Who should advice and monitor the technological development of AI?”
popAI is funded by the Horizon 2020 Framework Programme of the European Union for Research and Innovation. GA number: 101022001.
Educational Video 7
This video remarks the impact of AI on citizens’ perspective regarding its use by the police.
popAI is funded by the Horizon 2020 Framework Programme of the European Union for Research and Innovation. GA number: 101022001.
Educational Video 8
In this video, one of the most important questions is presented: “How well does AI meet police needs?”
popAI is funded by the Horizon 2020 Framework Programme of the European Union for Research and Innovation. GA number: 101022001.
Technology Ethics Briefs
The rapid advancement of technology brings with it countless opportunities to improve various aspects of society, such as predicting crime hotspots and digitizing old documents, to enhance public safety and efficiency. However, the use of technology in these areas also raises ethical dilemmas and considerations that must be carefully examined. This is particularly true in the field of law enforcement, where the application of technologies like predictive analytics, image recognition, and natural language processing can significantly impact privacy, civil liberties, and the potential for biased outcomes. In this series of three ethics briefs, we will explore how artificial intelligence is used in law enforcement, specifically focusing on predictive analytics, natural language processing (NLP), and image recognition. The briefs are focused to provide better awareness and information about the various uses and applications of artificial intelligence, including the potential benefits and risks of these technologies in policing, and to consider the ethical implications of their use.
Predictive Analysis
This brief talks about predictive analysis applied into the LEAs. Predictive analytics in policing consists of advanced data analysis techniques to identify patterns and predict future crime and public safety events. These techniques involve the application of machine learning algorithms to predict and identify potential crime hotspots, emerging crime trends, or individuals who may be at risk of committing a crime. Predictive analytics in policing can improve law enforcement, but it also raises some critical concerns related to privacy, fairness, bias, and accountability.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
This brief is about Natural Language Processing (NLP). This field of knowledge involves processing linguistic data to identify keywords and phrases from audio data and free-form text. This technology aims to make machines capable of reading and reasoning human language and automatically processing it. Some examples include information extraction, document categorisation and semantic text matching. NLP can help police agencies in crime investigations, intelligence gathering, and public safety operations through social media and other online platforms.
Image recognition
This brief includes image recognition algorithms. Image recognition is a computer vision process that involves identifying, detecting, and categorizing objects, patterns, or concepts in digital images or photographs. This process typically involves training a model on a labelled image dataset to later analyze and classify new images based on the learned patterns. In policing, image recognition is used to analyze and classify images or video footage obtained from cameras or other visual sources. Law enforcement agencies can benefit from this technology to identify suspects, track criminal activity, and ensure public safety. However, it’s crucial to use this technology ethically and implement appropriate safeguards to protect individual privacy and civil liberties.
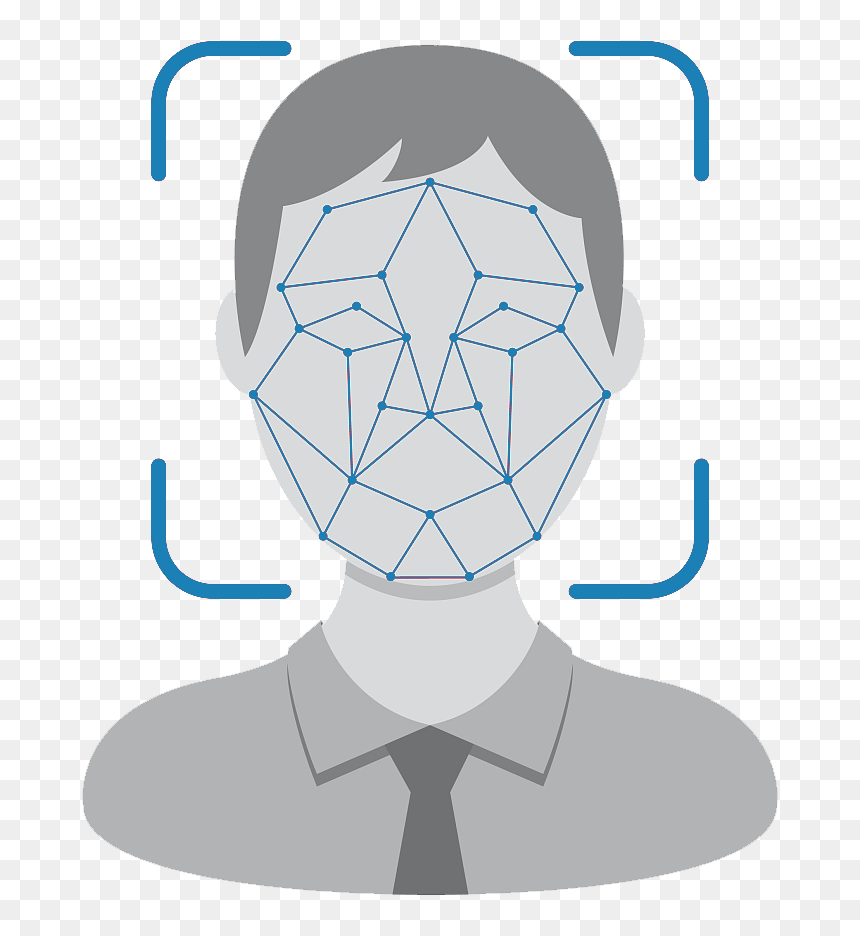
Taxonomies
The use of AI in LEAs has become increasingly prevalent in recent years. However, the use of AI in policing raises many ethical concerns that need to be addressed. In order to better understand and organize the field of AI and LEAs ethics, an interactive taxonomy has been developed. This taxonomy is not intended to be a comprehensive list, but rather a categorization framework for organizing relevant documents around AI in policing from four different perspectives: legal, ethics, functionalities, and social controversies.
The legal taxonomy is composed of laws, conventions, rights, guides or recommendations regarding the use of AI by Law Enforcement Agencies. The ethics component includes codes of ethics, recommendations, principles, policies and guidelines. The social taxonomy is enriched by local or national contributions in the field of LEAs, ethics and AI. Lastly, the functionality taxonomy is composed by several cases of the application of AI systems and models, for example image recognition, classification models, risk assessments, and more. In this sense, the taxonomies is the collection of multiple sources of information to facilitate the introduction to complex topics as AI, ethics and LEAs.
Taxonomies data tables
You can download the complete version of the taxonomies in a spreadsheet file. The elements are integrated in a single data table identified by their categories and correspondent links and references.